This article provides an online calculator for the Belt or Roller Mechanism to quickly find the servo’s electronic gear ratio and provide additional simulation information to evaluate whether the system parameters meet the requirements. The steps are as follows:
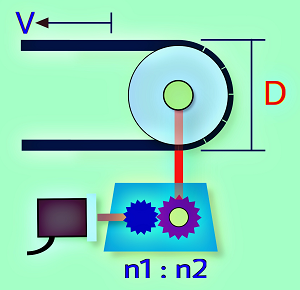
- Define user units(PUU), eg, How many PUUs correspond to 1 mm
- Enter the mechanical Reduction ratio (1:1 without deceleration)
- Enter the diameter(D) or circumference of the pully, including the belt.
- Enter Encoder Resolution(PLS), PLS number per turn of the Encoder,ie,when the electronic gear ratio is 1:1, how many PUUs the drive has to receive in order to rotate 1 turn.
- Press the “Calculate” button to get the numerator and denominator of the E-Gear Ratio
- Select “Significant digit number“: to specify the numeric width of the numerator, suggest 6 or above [Note 1].
- Enter the Line Speed(V) of the machine to check if the simulation results meet the requirements ?